Delving into the realm of insurance premiums, we uncover the reasons for their soaring prices and the impact on individuals.
Exploring income funds, index funds, inflation hedges, and more, we unravel the complexities of rising insurance costs.
Income Funds

Income funds are investment funds that primarily focus on generating income for investors through dividends, interest payments, and other sources of regular income. These funds typically invest in fixed-income securities such as bonds, preferred stocks, and money market instruments. Unlike growth funds that aim for capital appreciation, income funds prioritize providing a steady stream of income to investors.
Popular Income Funds
- Vanguard High Dividend Yield Index Fund (VHDYX): This fund focuses on high-dividend-yielding stocks of large U.S. companies.
- PIMCO Income Fund (PONAX): Managed by PIMCO, this fund invests in a diversified portfolio of fixed-income securities.
- Fidelity Strategic Dividend & Income Fund (FSDIX): This fund seeks income and capital appreciation by investing in dividend-paying stocks and fixed-income securities.
Benefits and Risks of Investing in Income Funds
Benefits:
- Steady Income: Income funds provide a consistent stream of income, making them attractive for investors seeking regular payouts.
- Diversification: These funds typically hold a variety of income-generating assets, which can help reduce risk through diversification.
- Professional Management: Income funds are managed by experienced professionals who make investment decisions to maximize income for investors.
Risks:
- Interest Rate Risk: Income funds are sensitive to changes in interest rates, which can impact the value of fixed-income securities in the fund.
- Credit Risk: There is a risk that issuers of the securities held by the fund may default on their payments, leading to potential losses.
- Inflation Risk: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of the income generated by the fund over time.
Index Funds
Index funds are a type of mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that is designed to track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average. These funds aim to replicate the performance of the index they are tracking by holding the same stocks in the same proportions as the index itself.
Performance and Fees
Index funds are passively managed, meaning they do not require a team of analysts to actively buy and sell securities. This passive management approach results in lower fees compared to actively managed funds, where fund managers make investment decisions in an attempt to outperform the market. While actively managed funds may sometimes outperform the market, they often come with higher fees and can have difficulty consistently beating the returns of the overall market.
- Index funds typically have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds, which can eat into an investor’s returns over time.
- Research has shown that over the long term, index funds tend to outperform actively managed funds due to their lower fees and more consistent performance.
- By tracking a specific market index, index funds provide investors with broad market exposure and diversification, reducing the risk associated with individual stock picking.
Inflation Hedge
Insurance premiums can serve as a valuable hedge against inflation, helping individuals protect their finances from the eroding effects of rising prices. As inflation reduces the purchasing power of money over time, insurance premiums act as a form of financial protection by providing coverage for unforeseen events.
Impact of Inflation on Insurance Premiums and Policy Coverage
Inflation can have a significant impact on insurance premiums, leading to higher costs for policyholders. As the cost of goods and services increases due to inflation, insurance companies may adjust their premiums to account for the rising expenses associated with providing coverage. This can result in policyholders paying more for their insurance policies to maintain adequate protection.Moreover, inflation can also affect the coverage provided by insurance policies.
In times of high inflation, the value of insurance coverage may decrease in real terms, as the sum assured or benefits may not be sufficient to cover the rising costs of goods and services. This can leave policyholders financially vulnerable if they experience a loss or damage that exceeds the coverage provided by their insurance policy.
Strategies to Protect Finances from Inflation through Insurance
- Consider purchasing inflation-adjusted insurance policies that automatically increase the coverage amount or sum assured to keep pace with inflation.
- Regularly review and update your insurance policies to ensure that the coverage provided is adequate to meet your financial needs in the face of inflation.
- Diversify your insurance portfolio to include a mix of policies that offer different types of coverage, such as health insurance, life insurance, and property insurance, to mitigate the impact of inflation on your overall financial security.
- Work with a financial advisor to develop a comprehensive insurance strategy that takes into account the effects of inflation and helps you protect your finances effectively.
Insurance Premiums

Insurance premiums can be a significant expense for individuals and businesses alike. Understanding the factors that contribute to high insurance premiums and knowing how to potentially lower them can help you make informed decisions when choosing insurance coverage.
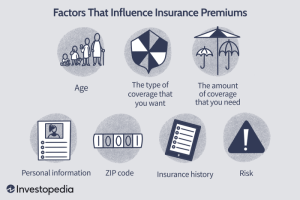
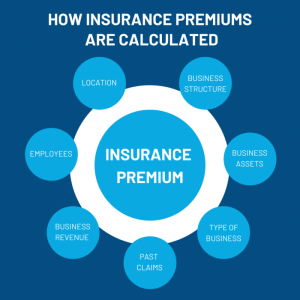
Factors Contributing to High Insurance Premiums
- Claims History: Insurance companies consider your past claims history when determining your premiums. If you have a history of filing frequent or costly claims, your premiums are likely to be higher.
- Location: Where you live can impact your insurance premiums. Areas prone to natural disasters or high crime rates may have higher premiums to account for increased risk.
- Type of Coverage: The type and amount of coverage you choose can affect your premiums. More comprehensive coverage typically comes with higher premiums.
- Age and Gender: Younger individuals and males tend to pay higher premiums for certain types of insurance, such as car insurance.
Reasons for Increasing Insurance Premiums
- Inflation: Rising costs due to inflation can lead to higher insurance premiums over time. Insurance companies may adjust their rates to account for increased expenses.
- Changes in Risk Factors: If the risk associated with insuring you or your property increases, such as a history of accidents or changes in your health, your premiums may go up.
- Market Conditions: Insurance premiums can be influenced by overall market conditions, such as the frequency and severity of claims across the industry.
Ways to Lower Insurance Premiums
- Shop Around: Compare quotes from different insurance companies to find the best rates for the coverage you need.
- Bundle Policies: Consider bundling multiple insurance policies with the same provider to potentially receive discounts on your premiums.
- Improve Your Credit Score: A higher credit score is often associated with lower insurance premiums, so work on improving your credit to potentially lower your rates.
- Review and Adjust Coverage: Periodically review your insurance coverage to ensure you’re not paying for more than you need. Adjusting your coverage can help lower your premiums.
In conclusion, the intricate web of factors influencing insurance premiums sheds light on the challenges individuals face in managing their financial security.
FAQ Explained
Why do insurance premiums keep increasing?
Insurance premiums rise due to factors like increased claims, inflation, and changes in risk profiles.
Can I lower my insurance premiums?
You may be able to reduce premiums by adjusting coverage, raising deductibles, or improving your risk profile.
How do income funds impact insurance premiums?
Income funds indirectly affect premiums by influencing investment returns for insurance companies.