Delve into the realm of insurance premiums as we uncover the various elements that can cause your rates to rise. From lifestyle choices to claim history, this comprehensive guide sheds light on the key factors affecting your insurance costs.
Learn how your decisions, circumstances, and even financial choices play a pivotal role in determining the premiums you pay.
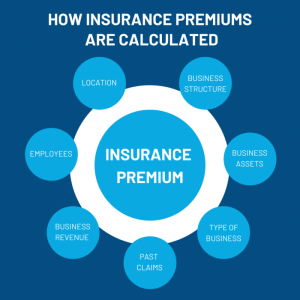
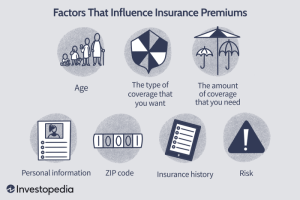
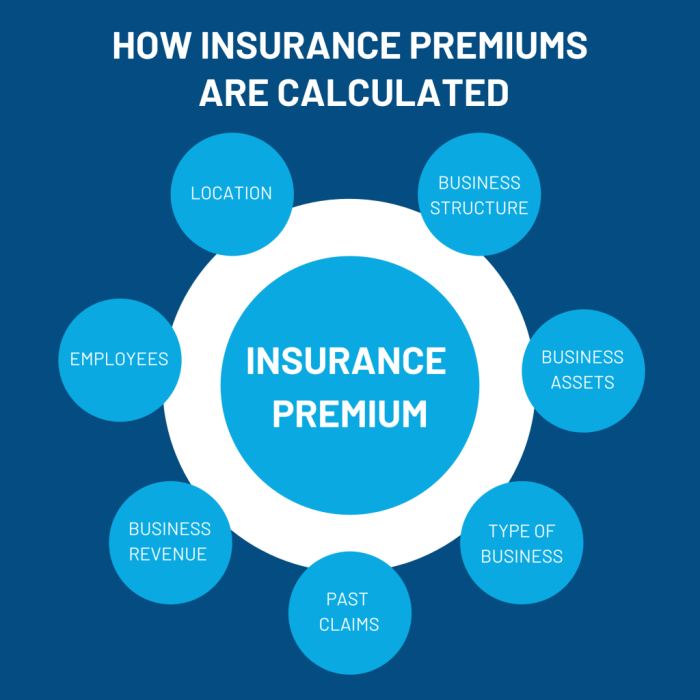
Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums
Age, gender, location, driving record, lifestyle choices, coverage type, and deductible amount are all factors that can significantly impact insurance premiums.
Demographic Factors
- Age: Younger drivers typically pay higher premiums due to less driving experience and higher risk of accidents.
- Gender: Statistics show that males tend to have more accidents than females, resulting in higher premiums for men.
- Location: Urban areas with higher crime rates or traffic congestion may lead to increased premiums.
Lifestyle Choices
- Smoking: Tobacco users may face higher premiums due to health risks associated with smoking.
- Risky Activities: Engaging in extreme sports or dangerous hobbies can also raise insurance costs.
Coverage and Deductible
- Type of Coverage: Opting for comprehensive coverage or adding extras like roadside assistance will increase premiums.
- Deductible Amount: Choosing a lower deductible means higher out-of-pocket costs in the event of a claim but lower premiums.
Types of Insurance Policies

Health insurance, auto insurance, home insurance, and life insurance are all different types of insurance policies that individuals can purchase to protect themselves and their assets. Each type of policy has its own unique factors that influence premium calculation.
Health Insurance
Health insurance premiums are typically calculated based on factors such as age, location, and health history. Policy limits, coverage options (such as deductibles and copayments), and add-ons (such as dental or vision coverage) can all impact the cost of health insurance premiums. For example, a health insurance policy with a lower deductible and broader coverage options will generally have a higher premium compared to a policy with a higher deductible and more limited coverage.
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance premiums are determined by factors such as the driver’s age, driving record, location, and the type of vehicle being insured. Policy limits, coverage options (such as comprehensive and collision coverage), and add-ons (such as roadside assistance or rental car coverage) can also affect auto insurance premiums. Bundling multiple vehicles or policies with the same provider can often lead to discounts on premium rates.
Home Insurance
Home insurance premiums are influenced by factors like the location of the home, the age and condition of the property, and the coverage limits selected. Additional factors such as the presence of safety features (like smoke alarms or security systems) and add-ons (such as flood insurance or personal property coverage) can impact home insurance premiums. Bundling home and auto insurance policies with the same provider can result in savings on premium rates.
Life Insurance
Life insurance premiums are typically based on factors like the insured individual’s age, health, and lifestyle habits. Policy limits, coverage options (such as term or whole life insurance), and add-ons (like riders for additional coverage) can all affect life insurance premiums. Bundling life insurance with other insurance policies from the same provider may also lead to discounted premium rates.
Insurance Claim History
When it comes to determining insurance premiums, your claim history plays a significant role. Insurance companies assess the risk associated with insuring you based on your past claims.
Frequency of Insurance Claims
- A history of frequent insurance claims indicates a higher likelihood of future claims, which can lead to increased premiums.
- Insurance companies view frequent claimants as higher risk policyholders, as they are more likely to incur costs for the insurer.
Impact of Filing Claims for Minor Incidents
- Even filing claims for minor incidents, such as a small fender bender or minor damage, can impact your future premium costs.
- Insurance companies may consider you a higher risk if you have a pattern of filing claims for minor issues, potentially leading to higher premiums.
No-Claim Bonuses and Discounts
- No-claim bonuses or discounts are incentives offered by insurance companies to policyholders who do not file any claims during a policy term.
- By maintaining a clean claims record and not filing for minor incidents, policyholders can benefit from reduced premiums through these bonuses and discounts.
Credit Score and Insurance Premiums
Maintaining a good credit score can have a significant impact on your insurance premiums. Insurance companies often consider credit score as a factor when calculating premiums for various types of insurance policies. Your credit score can influence the risk level associated with insuring you, which in turn affects the amount you pay for coverage.
Influence of Credit Score on Insurance Premiums
- Insurance companies use credit scores to predict the likelihood of a policyholder filing a claim.
- Individuals with higher credit scores are seen as less risky to insure, leading to lower premiums.
- Conversely, those with lower credit scores may be charged higher premiums due to the perceived higher risk.
Maintaining a Good Credit Score for Lower Premiums
- Make timely payments on credit accounts to avoid negative impacts on your credit score.
- Keep credit card balances low and avoid opening multiple new accounts within a short period.
- Regularly monitor your credit report for errors and address any issues promptly.
Reasons for Considering Credit Score in Premium Calculation
- Insurance companies believe that individuals with higher credit scores are more responsible and less likely to file claims.
- Studies have shown a correlation between credit score and insurance risk, influencing premium calculations.
- Using credit scores allows insurers to assess risk more accurately and set premiums accordingly.
Personal Factors Impacting Premiums
Occupation, education level, marital status, number of dependents, and household income are all personal factors that can have an impact on insurance premiums. Insurance companies take these factors into account when determining the rates for individuals.
Occupation
Different occupations may have varying levels of risk associated with them, which can influence insurance premiums. For example, individuals working in high-risk professions such as construction or law enforcement may face higher premiums compared to those in low-risk jobs like office administration.
Education Level
Insurance companies often consider education level as a factor in determining premiums. Studies have shown that individuals with higher education levels tend to file fewer claims, leading to potentially lower premiums for those with advanced degrees.
Marital Status
Marital status can also impact insurance premiums. Married individuals may be eligible for discounts or lower rates compared to single individuals. This is because married couples are perceived as more stable and responsible, leading to potentially lower risk for insurance companies.
Number of Dependents
The number of dependents a policyholder has can affect insurance premiums. More dependents may lead to higher premiums since there is a higher likelihood of claims being filed to cover the needs of the family members.
Household Income
Insurance companies may also consider household income when determining premiums. Higher household incomes may indicate a greater ability to pay for insurance coverage, potentially resulting in lower premiums. Conversely, lower incomes may lead to higher premiums or limited coverage options.
Income Funds vs. Index Funds
Income funds and index funds are two popular investment options with distinct characteristics and strategies. Income funds primarily focus on generating regular income for investors through dividends and interest payments, while index funds aim to track a specific market index and offer diversification benefits.
Risk and Return Potential
Income funds typically have lower risk compared to index funds, as they invest in fixed-income securities such as bonds and preferred stocks. While income funds provide steady income streams, they may offer lower return potential compared to index funds, which are often linked to the performance of the overall market.
Investment Strategy
Income funds are managed with the goal of generating consistent income for investors, making them suitable for those seeking regular payouts. These funds often prioritize stability and income generation over capital appreciation. On the other hand, index funds passively track a specific market index, aiming to replicate its performance. This passive investment strategy results in lower management fees compared to actively managed funds.
Dividends and Interest Payments
Income funds generate returns for investors through dividends from stocks and interest payments from bonds held in the fund’s portfolio. These funds distribute a significant portion of their earnings to investors in the form of regular income payments. Investors looking for a steady income stream often opt for income funds due to their income-generating focus.
Diversification Benefits
Index funds offer diversification benefits to investors by providing exposure to a wide range of securities within a specific market index. By investing in an index fund, investors gain access to a diversified portfolio without the need to select individual stocks or bonds. This diversification helps reduce risk by spreading investments across different assets within the index.
Inflation Hedge Strategies

Inflation can erode the value of investments over time, making it crucial for investors to consider strategies to hedge against inflation. Various approaches exist to mitigate the impact of rising prices on investment portfolios.
Real Assets as Inflation Hedges
- Real Estate: Investing in physical properties can serve as an inflation hedge, as property values tend to increase with inflation.
- Commodities: Assets like gold, silver, oil, and other commodities can act as a store of value during inflationary periods.
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
- Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) are government bonds designed to protect against inflation. The principal amount adjusts based on changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), ensuring that investors receive a return above inflation.
- Investors can consider including TIPS in their portfolios to maintain purchasing power and safeguard against the erosive effects of inflation.
Understanding Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums are the amount of money an individual or business pays to an insurance company for coverage. These premiums are calculated based on various factors and help the insurance company manage risk and provide financial protection to the policyholder in case of unexpected events.
Types of Insurance Premiums
- Annual Premiums: These are one-time payments made for a year’s worth of coverage.
- Monthly Premiums: These are smaller payments made each month for ongoing coverage.
- Semi-Annual Premiums: These are payments made every six months for coverage.
Factors Affecting Premium Rates
- Age and Gender: Younger individuals and males typically pay higher premiums due to higher risk.
- Driving Record: A history of accidents or traffic violations can increase auto insurance premiums.
- Location: Living in an area prone to natural disasters or high crime rates can lead to higher premiums.
- Type of Coverage: More comprehensive coverage options often come with higher premiums.
- Claim History: Individuals who have filed multiple claims in the past may face increased premiums.
In conclusion, understanding what drives your insurance premiums up is the first step towards making informed decisions about your coverage. By grasping the intricacies of this complex system, you can navigate the insurance landscape with confidence and clarity.
Key Questions Answered
How can my credit score impact my insurance premiums?
Your credit score can influence your insurance premiums as insurance companies view it as a reflection of your financial responsibility. A higher credit score often leads to lower premiums.
Can my occupation affect how much I pay for insurance?
Yes, your occupation can impact your insurance premiums. Certain professions may be considered riskier by insurance companies, leading to higher premium costs.
What is the role of no-claim bonuses in reducing insurance premiums?
No-claim bonuses are rewards offered by insurance companies to policyholders who do not make any claims during a policy year. These bonuses can lead to discounts on future premiums.