Kicking off with Impact of Credit Score on Insurance Premiums, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone for the discussion ahead. Exploring how credit scores can significantly affect insurance premiums, this topic delves into the intricate relationship between financial health and insurance costs.
Moving forward, we will delve into the specifics of how credit scores play a crucial role in determining insurance premium rates, shedding light on the impact of both low and high credit scores on the financial aspects of insurance policies.
Impact of Credit Score on Insurance Premiums

Having a good credit score can positively impact your insurance premiums by potentially leading to lower rates. On the other hand, a low credit score can result in higher insurance premiums due to the perceived risk associated with poor credit history.
Low Credit Score Impact
A low credit score can significantly impact insurance premium rates as insurance companies may view individuals with poor credit history as higher risk policyholders. This can result in higher premiums for auto, home, or even health insurance policies.
- Insurance companies may consider individuals with low credit scores as more likely to file claims, leading to increased premiums to offset the perceived risk.
- Policyholders with low credit scores may be charged higher rates or even denied coverage altogether in some cases.
- For example, a driver with a low credit score may end up paying significantly more for car insurance compared to someone with a higher credit score, even if they have similar driving records.
High Credit Score Benefits
Conversely, individuals with high credit scores often enjoy lower insurance premiums due to the perception of being more financially responsible and less likely to file claims.
- Insurance companies may offer discounts or lower rates to policyholders with high credit scores as they are seen as lower risk customers.
- For instance, a homeowner with an excellent credit score may qualify for lower premiums on their homeowner’s insurance policy compared to someone with a lower credit score.
- Having a high credit score can also result in better insurance options and more competitive rates across various types of insurance coverage.
Income Funds
Income funds are investment vehicles that primarily focus on generating income for investors through interest payments, dividends, or other distributions. These funds typically invest in fixed-income securities such as bonds, preferred stocks, or other debt instruments.
Comparison with Other Investments
Income funds are often considered lower risk compared to other types of investments such as stocks because they prioritize generating a steady income stream for investors. While the potential returns may be lower than riskier investments like equities, income funds provide a more stable source of income over time.
Benefits of Investing in Income Funds
- Stable Income: Income funds can provide a reliable source of income for investors, making them suitable for individuals looking to supplement their earnings or fund their retirement.
- Diversification: By investing in a variety of fixed-income securities, income funds help spread risk and reduce the impact of market fluctuations on the overall portfolio.
- Capital Preservation: Income funds prioritize preserving capital while generating income, making them a conservative option for investors concerned about protecting their principal investment.
- Long-Term Financial Goals: Investing in income funds can help individuals achieve their long-term financial goals by providing a steady stream of income and potential capital appreciation over time.
Index Funds
Index funds are a type of mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that tracks a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These funds aim to replicate the performance of the index they are based on, rather than trying to outperform it like actively managed funds. This passive investment approach typically results in lower management fees and expenses compared to actively managed funds.
Advantages of Investing in Index Funds for Beginners
Index funds offer several advantages for beginners looking to start investing:
- Low Cost: Index funds generally have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds, making them a cost-effective option for beginners.
- Diversification: By investing in an index fund that tracks a broad market index, beginners can achieve instant diversification across multiple companies and sectors.
- Consistent Performance: Index funds aim to replicate the performance of the underlying index, providing a more predictable investment return over the long term.
- Easy to Understand: Index funds are straightforward investment vehicles that are easy for beginners to understand, making them a good starting point for those new to investing.
How Index Funds Can Help in Diversifying a Portfolio Effectively
Diversification is a key principle in investing to reduce risk and maximize returns. Index funds can help in diversifying a portfolio effectively by:
- Exposure to Various Sectors: Investing in an index fund that tracks a broad market index provides exposure to multiple sectors of the economy, reducing the impact of sector-specific risks.
- Automatic Rebalancing: Index funds automatically rebalance their holdings to mirror the composition of the underlying index, ensuring that the portfolio remains diversified over time.
- Risk Management: Diversifying with index funds can help spread risk across different asset classes and geographies, reducing the overall volatility of the portfolio.
Inflation Hedge

Inflation hedge refers to investments that have the potential to maintain or increase their value over time, even when prices in the economy are rising. This is important in investment strategies as inflation can erode the purchasing power of money over time, making it crucial for investors to protect their portfolios from its effects.
Assets as Inflation Hedges
- Real Estate: Real estate properties tend to increase in value over time, acting as a hedge against inflation.
- Commodities: Assets like gold, silver, and other precious metals are often used as inflation hedges due to their intrinsic value.
- TIPS (Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities): These bonds are specifically designed to protect against inflation by adjusting their principal value based on changes in the Consumer Price Index.
Hedging Strategies
- Diversification: By spreading investments across different asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of inflation on their portfolios.
- Stocks and Equities: Investing in companies with strong pricing power and the ability to pass on cost increases to consumers can help protect against inflation.
- Interest Rate Hedges: Utilizing investments that benefit from rising interest rates can counteract the negative effects of inflation on fixed-income securities.
Insurance Premiums
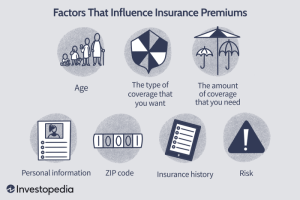
Insurance premiums are the amount of money an individual or business pays for an insurance policy. The cost of insurance premiums is influenced by various factors that help determine the level of risk associated with insuring the policyholder.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premium Calculations
- Age and Gender: Younger individuals are typically charged higher premiums as they are considered riskier to insure. Gender also plays a role in certain types of insurance where statistical differences exist.
- Health and Lifestyle: Factors such as pre-existing medical conditions, smoking habits, and occupation can affect health insurance premiums.
- Driving Record: Auto insurance premiums are influenced by factors such as driving history, vehicle type, and mileage.
- Location: Where you live can impact insurance premiums due to factors like crime rates, weather risks, and population density.
- Coverage Amount: The more coverage you require, the higher your insurance premium is likely to be.
Types of Insurance Premium Determination
- Auto Insurance: Premiums are often determined by factors such as driving record, age, gender, vehicle type, and coverage level.
- Health Insurance: Premiums are based on factors like age, pre-existing conditions, lifestyle habits, and coverage options.
- Life Insurance: Premiums are calculated based on age, gender, health status, smoking habits, and coverage amount.
Hypothetical Breakdown of Insurance Premium Components
| Component | Percentage Contribution |
|---|---|
| Age and Gender | 20% |
| Health and Lifestyle | 15% |
| Driving Record | 25% |
| Location | 10% |
| Coverage Amount | 30% |
In conclusion, the discussion on the impact of credit scores on insurance premiums highlights the vital importance of maintaining a good credit standing for favorable insurance rates. Understanding this correlation can empower individuals to make informed financial decisions that benefit their overall insurance costs and coverage.
User Queries
How does a credit score influence insurance premiums?
Insurance companies often use credit scores as a factor in determining premium rates, with lower credit scores leading to higher premiums. A good credit score can result in lower insurance costs.
What are some common examples of how a low credit score impacts insurance premium rates?
A low credit score can lead to increased insurance premiums, making coverage more expensive for individuals with poor credit histories.
How can a high credit score lead to lower insurance premiums?
Individuals with high credit scores are seen as less risky by insurance companies, resulting in lower premium rates as they are perceived to be more financially responsible.